但凡考试,都有一个准绳,这个准绳就是大纲。吃透大纲,才能保证方向正确,不走弯路。今天,医学教育网小编给新加入考博阵营的战友们科普一下全国医学博士英语统考的大纲,帮助大家快速了解考试时间、试卷结构、题型设置、试卷难度等基本情况。
一、考试目的
为了配合我国实施医学专业学位制定改革,保证医学博士生学位授予质量,特举行全国医学博士英语统一考试。考试目的在于科学、公正地测试考生掌握和运用英语的实际能力是否达到申请临床医学、口腔医学博士专业学位或攻读医学博士学位的英语水平。
二、考试设计
本考试主要是用于医学博士生入学和申请医学博士专业学位的一种英语水平考试,其命题不以任何一种医学英语教材为命题依据。
考试内容为医学公共英语,注重突出临床医学特点。
本考试从听力、词语用法、综合理解、阅读和书面表达五个方面命题,全面测试考生的英语能力,并突出对考生的英语应用和交际能力测试,以确定其是否已达到在职申请医学博士专业学位的英语水平或是否已达到医学博士研究生入学英语水平。
三、试卷结构
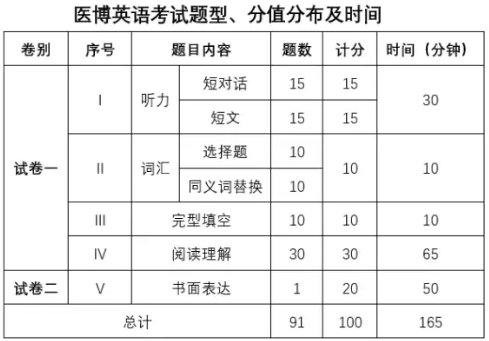
试卷分为两大部分:试卷一(Paper One)和试卷二(Paper Two)。
试卷一包括听力(30%),词语用法(10%),完型填空(10%)和阅读理解(30%),答卷时间115分钟;试卷二包括书面表达(20%),答卷时间 50 分钟,整个试卷共五大部分,总分 100 分,答卷时间共 165 分钟,加上考场指令与试卷收发时问,总共考试时间 180 分钟。
试卷一(Paper One)
I. 听力理解 (Listening Comprehension)
听力分两部分 Section A 和 Section B。答题时间为 30 分钟。
Section A:简短对话(Short Conversations)
简短对话旨在测试考生的英语听力能力,要求考生在听完每个对话之后,根据所听内容于 12 秒钟内对每个问题后的四个选择项做出正确选择,每个对话及提问只读一遍。
本部分共 15 小题,编号为 1-15,每题 1 分,共计 15 分。例:
听力录音:
M: The immunizations are being given at the end of the hall.
W: But I just came from that direction, and I didn't see any nurses. I didn't see any nurses downstairs either.
Q: What is the woman's problem?
听力试题:
A. She is on the wrong floor.
B. She does not know any nurse.
C. She cannot find the immunization area.
D. She received an immunization too late.
(答案:C)
Section B: 长对话及短文(Long Conversations and Talks)
本部分由一篇长对话和两篇短文组成,旨在测试考生对英语篇章的听力理解能力。要求考生能理解所听材料的中心思想和主要内容,并能根据所听到的内容进行逻辑推理、分析概括和归纳总结。
每篇材料后附有 5 个问题,每个问题后均有四个选择项。要求考生在听完每个问题后,于 12 秒钟内从中选出一个最佳答案。每篇材料及提问只读一遍。
该部分共 15 小题,编号为 16-30,每题 1 分,共计 15 分。例:
长对话听力录音
W: We have been going round the country interviewing people about their jobs, Mr. Wills, and we would like to know something about your work as a dentist. May we ask you some questions about your practice here in Little Smattering?
M: Of course you may. But you mustn't take too long as I have another patient arriving in about ten minutes.
W: I'll be as quick as I can. What made you decide to become a dentist?
M: Oh, I don't think there was ever any doubt about it. My father was a dentist in this little town all his life, and it was always taken for granted that I would take over his practice when he retired.
W: How long did you have to study before you qualified?
M: Five years. l was exempt from the preliminary year of the course, as I had passed physics, chemistry and biology at advanced level at school. So when I was nineteen I went to a dental school, which was attached to one of the larger London hospitals. The first two years of my course were spent studying anatomy, physiology and dental mechanics. During that time I was also taught how to make false teeth and all the other various appliances that are used in modem dentistry. The second part of the course, the last two years, was devoted to clinical practice in the hospital, and practical treatment of patients.
W: Were you allowed to practice on patients before you qualified?
M: Yes, but only after I had really learned what to do. Students spend many hours with a “phantom head"1473 that is a head made of plastic, which has teeth that can be extracted or filled. They practice for a long time with this before they are finally allowed to treat a real live patient.
W: When did you set up in practice here?
M: As soon as I had been admitted to the Dentists' Register, which happened shortly after I had passed my final examination.
Questions:
16. What is the woman's occupation?
17. Why did Mr. Wills decide to become a dentist?
18. When did Mr. Wills go to the dental school?
19. What courses did Mr. Wills have to learn in the dental school?
20. How long should students practice before they are finally allowed to treat a real live patient?
听力试卷
16. A. Journalist.
B. Dentist.
C. Headhunter.
D. Social worker.
17. A. Because he had always wanted to be a dentist.
B. Because he was interested in medicine.
C. Because he would follow his father's footsteps.
D. Because he took over his father's practice in Little Smattering.
18. A. Five years ago.
B. When he was nineteen.
C. After he passed a dental test.
D. After he passed a biology test at advanced level.
19. A. Physics, chemistry and biology.
B. Clinical practice in the hospital.
C. Making false teeth and other various appliances.
D. Anatomy, physiology and dental mechanics.
20. A. Few hours.
B. A long time.
C. Two years
D. Five years.
(答案: 16. A 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. B)
短文录音:
To quickly review the main points covered in Chapter Seven, the most important part of the system of nerve is the brain. The brain controls most of the body's activities. Messages between the brain and the spinal cord are carried by nerves, which are made up of special cells called nerve cells. Nerve cells are found in the brain, spinal cord, spinal nerves and the organs we use to see, hear, smell, taste and touch.
Nerve cells have long string-like fibers that carry messages. These fibers have branched ends to send and receive messages. Remember that nerve cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. But one fiber from a nerve cell may stretch as long as three feet.
There are many kinds of nerve cells, and this chapter deals mainly with three kinds. The sensory nerve cells carry messages of heat, light, sound and pressure from the skin, muscles and organs inside the body. Motor nerve cells carry messages to the muscles, and this causes the muscle to move. Connecting nerve cells go between the sensory nerve cells and motor nerve cells. After the messages go from the spinal cord to the brain, the brain sends messages through the motor nerve cells to the muscles. All these different nerve cells help us see, hear, taste, smell and feel.
Now if you have no further questions about Chapter Seven, we'll go on to talk about the chemical processes involved in this transfer of messages.
Questions 21-25 are based on the following questions:
21. What is the source of the speaker's information?
22. What role do nerve fibers play?
23. What does a nerve fiber look like according to the speaker?
24. How many kinds of nerve cells are discussed in this talk?
25. Which of the following nerve cells sends messages to the muscles?
听力试卷:
21. A. A medical textbook.
B. A medical journal.
C. Some microscope slides.
D. The speaker's current research.
22. A. Reproducing themselves.
B. Stretching and growing.
C. Attaching themselves to muscles.
D. Carrying messages.
23. A. Elongated and stringy.
B. Round and compact.
C. Flat and transparent.
D. Flexible and chainlike.
24. A. One. B. Two. C. Three. D. Four.
25. A. Sensory nerve cells.
B. Motor nerve cells.
C. Connecting nerve cells.
D. All of the above.
(答案:21. A 22. D 23. A 24. C 25. B)
II. 词语用法 (Vocabulary)
词语用法旨在测试考生对英语词汇和短语的理解和使用能力,分两部分:Section A 和 Section B。
Section A: 填空 (Fill in the blank)
该部分试题的题干为一个或两个句子,句中留有一处空白,题干后附四个选择项,要求考生从中选出一个最佳答案,填入题干后使该句子语法正确,逻辑合理,意思完整。
该部分共 10 小题,编号为 31-40,每题 0.5 分,共计 5 分。例:
31. The "City of Hope" in California is dedicated to relieving pain and prolonging life with ______.
A. expectancy
B. longevity
C. dignity
D. identity
(答案:31. C)
Section B:多选题 (Multiple choice)
该试题的题干为一个或两个句子,句中有一词或短语下面划有横线,题干后附四个选择项,要求考生从中选出一个和词中划线部分的意义相同或近似的最佳答案。本题测试的词语,不超出考试大纲所附词汇表的内容范围。
该部分共 10 小题,编号为 41-50,每题 0.5 分,共计 5 分。例:
41. You cannot burden your memory with too much information.
A. retain B. load C. retrieve D. associate
(答案:41. B)
III. 完型填空(Cloze)
本部分共 10 小题,计 10 分。考试时间 10 分钟。
此题着重测试考生在篇章水平上理解和运用语言的综合能力。要求考生阅读一篇约 200 词的英语短文,其中留有 10 处空白。每一空白附有四个选择项,考生在理解全文大意和上下文意思的基础上,从四个选择项中选出一个最佳答案,使短文在语法、用词、句型结构和上下文逻辑关系等方面都能完善。
该部分 10 个小题的编号为 51-60。例:
In June a Senate committee released its report on euthanasia and assisted suicide. A majority of its members recommended against legalizing the two procedures. As the public debate in this country intensifies, it is instructive to look at the Netherlands, where euthanasia, while not 51 , has been increasingly tolerated by the courts in recent years.
In the intensive-care unit of a Dutch hospital, a man lay with chronic leukemia 52 with pneumonia. His hands and feet were bound, and he was being respired with a tube in his throat. A young assistant physician appeared at his bedside and said, “I assume that if your heart fails, you don't want to be resuscitated."
Unable to talk, the man shook his head vehemently from left to right, the only movement he could make to 53 that indeed he did want to be resuscitated. Despite the seriousness of his illness, he knew he could still live for years. But the physician, misinterpreting his 54 , said, “That's assumed, then," made a note on the patient's chart and moved on.
The sick man was in a panic. Fortunately, 55 gestures, he managed to tell his son, who was able to prevent a tragic mistake.
This is an example of how increasingly casually doctors in the Netherlands are 56 the ending of life by withdrawing medical treatment—a procedure known 57 passive euthanasia. It is only one of many. Tom Schalken, professor of criminal law at the Free University of Amsterdam, was a member of a commission that 58 euthanasia in 1990. 0f an annual total of 130, 000 deaths, in 2,300 cases, physicians reported that euthanasia had been carried out at the 59 of the patient. But the commission 60 that in more than 1, 000 instances, physicians had ended a life without an explicit request for example, with patients in coma or newborn babies.
51. A. being legalized
B. legalizing
C. legalized
D. legalizes
52. A. connected
B. included
C. related
D. combined
53. A. indicate
B. notice
C. notify
D. appear
54. A. symptom
B. gesture
C. symbol
D. sign
55. A. by reason of
B. in place of
C. in the course of
D. by means of
56. A. dealing with
B. getting with
C. solving
D. coming over
57. A. for B. as C. of D. after
58. A. came into
B. looked into
C. went into
D. grew into
59. A. request
B. command
C. demand
D. recommend
60. A. ascertained
B. is ascertained
C. has ascertained
D. was ascertained
(答案:51. C 52. D 53. A 54. B 55. D 56. A 57. B 58. B 59. A 60. A)
IV. 阅读理解(Reading Comprehension)
本部分共 30 小题,计 30 分。考试时间 65 分钟。
该部分由 6 篇阅读短文组成。每篇短文约 300 个单词,后附 5 个问题,每个问题后均有四个选择项。
此类题目是测试考生通过阅读英文书刊获取信息的能力(包括阅读速度和理解程度)。要求考生在读完一篇文字材料后,能理解其主题思想、主要内容和主要细节。能根据所读材料的内容进行推理判断,理解某些词和短语在具体语境中的意义,理解句与句之间的内在逻辑关系能领会作者的观点和思想感情,判断其对事物的态度。测试材料主要是涉及医学科普、自然科普和人文等各种题材和体裁的文章。要求考生根据所读材料的内容,从每道题的选择项中选出一个最佳答案。
该部分 30 个小题的编号为 61-90。例:
Passage one
It has almost become dogma that athletes require greater amounts of protein than sedentary individuals. In addition to eating more protein, athletes also need to be aware of the times of day at which they consume both different types and amounts of protein. The post-workout meal is one of the most important times and meals of the day regarding protein intake. Researchers have shown that eating a protein-rich meal at this time can greatly increase protein synthesis and possibly muscle growth.
In one study, subjects were given an intravenous protein supplement following either a period of exercise or rest. Protein synthesis was then measured in each subject to determine how the different types of activities affected protein synthesis. Results from the study concluded that protein synthesis was doubled in the subjects who had just performed a session of strength-training exercise. The researchers in this study concluded that this was more than likely due to the increase in blood flow to the subject's muscles following exercise.
Since the rate of protein synthesis and possibly muscle growth can double when protein is consumed post-workout it is imperative that a meal containing quality proteins be consumed at this time.
When determining protein types for a post-workout meal, whey protein makes an excellent choice. The reason for this is that whey protein contains the best amino acid profile of all protein types and is also absorbed at a very rapid rate by the body.
61. In order to meet the need of the body for protein, an athlete should ___________.
eat better than non-athletes
have different meal time from that of the average person
increase protein synthesis and muscle growth
have a special dietary plan
62. In the first paragraph the author points out that ________________.
a protein-rich meal is very important for athletes after some exercise
a good meal is necessary for athletes before working outside
the post-workout meal is usually rich in protein
researchers can increase protein synthesis by eating protein-rich meals
63. The purpose of the study as mentioned in the second paragraph is _________.
to double protein synthesis
to see how protein synthesis takes place
to establish the relationship between physical activities and protein synthesis
to measure the participants' blood flow to the muscles
64. According to the passage, which of the following is true?
Muscle grows faster after a post-workout meal.
Protein supplement should be given after exercise.
Physical activities will affect a man's rate of protein synthesis.
The body absorbs whey protein more quickly than other types of proteins.
65. What is the possible topic of the passage?
Athletes and Food.
Sports and Protein.
Protein Synthesis and Exercise.
Protein after Exercise.
(答案: 61. D 62. A 63. C 64. C 65. D)
试卷二(Paper Two)
V. 书面表达(Writing)
本部分计 20 分,考试时间 50 分钟。此部分旨在测试考生使用英语书面表达自己思想的能力。测试设计以下两种方式,每年任选其中一种。
1. 文章摘要
要求考生阅读一篇 800-1000 字的汉语文章后,用英语写出一篇约 200 个单词的摘要。所概括的内容应简洁、全面、准确,文字应通顺,基本符合英语表达习惯,无重大语法错误。
2. 翻译与写作
本部分包括段落翻译与段落写作。翻译应忠实原文。作文要求切题,意思连贯。无论是翻译还是作文均要求文字通顺,基本符合英语表达方式。
以上就是我为大家整理的来自官方的全国医学博士英语统一考试大纲,还请大家多多关注医学教育网,我们会随时更新更多更好的有关医学考试、医疗招聘、辅导资料等相关内容,敬请期待!











 扫一扫立即下载
扫一扫立即下载


